Understanding Crypto Trading High-Frequency
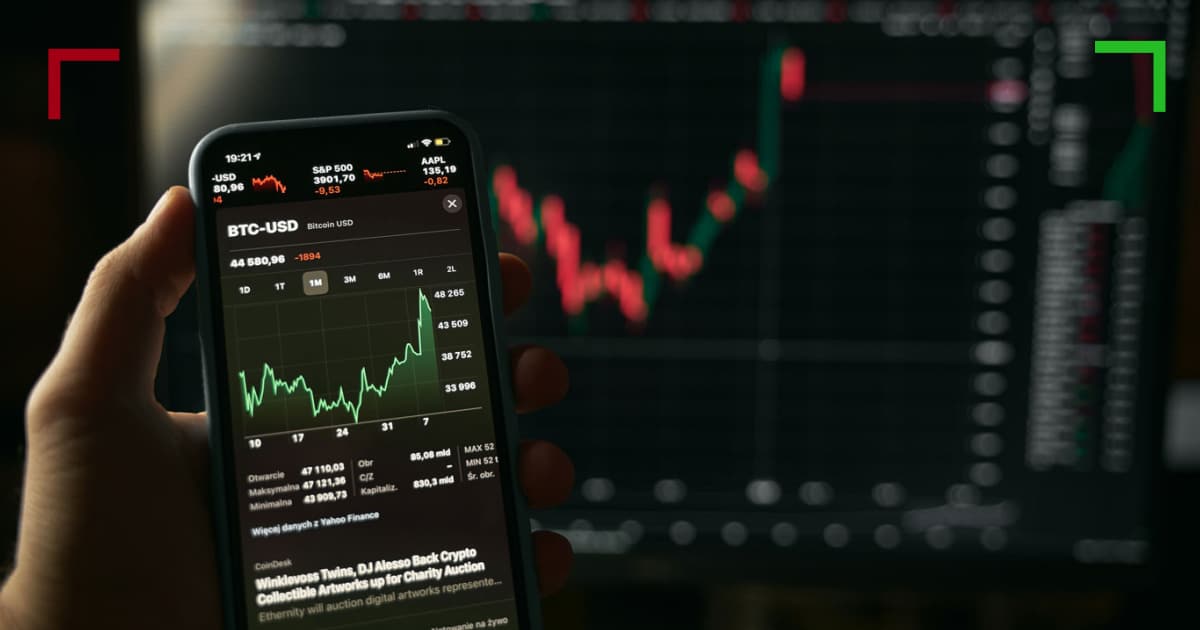
High-frequency trading (HFT) has emerged as a pivotal component within the world of cryptocurrency trading. With the rapid evolution of technological advancements over the past decade, traders are increasingly leveraging sophisticated algorithms and powerful computing resources to execute trades at lightning speed. This article delves into the intricate dynamics of Crypto Trading High-Frequency, uncovering the strategies, tools, and the broader implications for the future of trading. In the landscape of cryptocurrency trading, the stakes are high, and understanding the mechanics behind high-frequency trading can distinguish successful traders from the rest. For further insights and discussions on the financial aspects of the crypto domain, you may refer to this article: Crypto Trading High-Frequency https://archive.globalcoinresearch.com/2019/01/01/joyce-yang-founder-of-global-coin-research-to-speak-columbia-universitys-blockchain-conference-ledgerfest/.
What is High-Frequency Trading?
High-frequency trading refers to the use of advanced electronic trading tools to execute a large number of orders at extremely high speeds. HFT is characterized by its ability to conduct thousands of trades in a fraction of a second, capitalizing on small price discrepancies across various markets. In the context of cryptocurrencies, HFT allows traders to take advantage of the market’s inherent volatility, offering the potential for substantial profits.
The Mechanics of High-Frequency Trading
High-frequency trading in the crypto market requires a robust infrastructure, including high-speed internet, powerful hardware, and sophisticated software algorithms. Traders typically employ quantitative methods to analyze vast amounts of market data, identifying patterns and trends that inform their trading strategies. Algorithms are designed to execute trades automatically, minimizing human intervention and reducing the time between signal and execution.
Infrastructure and Technology
The backbone of HFT is its technological infrastructure. Many successful high-frequency traders use co-location services, which place their trading servers in close physical proximity to cryptocurrency exchanges. This reduces latency, allowing for faster execution of trades. Additionally, traders utilize custom-built algorithms programmed to process large datasets in real time, making split-second decisions based on predetermined criteria.
Trading Strategies
HFT strategies can vary significantly, but some of the most common methods employed include:
- Arbitrage: This involves exploiting price discrepancies between different exchanges or markets. For instance, if Bitcoin is trading at a lower price on one exchange compared to another, a high-frequency trader can purchase it on the cheaper exchange and sell it on the more expensive one almost instantaneously.
- Market Making: Market makers provide liquidity to the market by placing buy and sell orders. They profit from the bid-ask spread, consistently placing themselves in a position to profit as prices fluctuate.
- Trend Following: Some HFT strategies focus on identifying and following trends in cryptocurrency prices using various technical analysis tools. Traders can capitalize on short-term price movements driven by market sentiment or news.
The Benefits and Risks of High-Frequency Trading
While the advantages of HFT are numerous, including the potential for high returns and market efficiency, there are also significant risks involved.
Benefits
- Speed: HFT’s ability to execute trades faster than human traders allows for taking advantage of fleeting opportunities.
- Efficiency: HFT can increase market liquidity, making it easier for other traders to enter and exit positions.
- Profit Potential: The ability to execute numerous trades can lead to significant cumulative profits over time.
Risks
- Market Volatility: The cryptocurrency market is known for its volatility, which can lead to rapid losses if trades don’t go as planned.
- Technical Failures: HFT relies heavily on technology, and any technical glitches can result in significant losses or missed opportunities.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: As HFT becomes more prevalent, regulatory bodies may impose stricter regulations that could impact trading strategies.
Future of High-Frequency Trading in Cryptocurrencies
The future of high-frequency trading in the cryptocurrency arena looks promising, driven by continued advancements in technology and increased institutional interest. As blockchain technology matures and more financial institutions delve into the crypto space, the infrastructure supporting HFT will likely evolve.
Institutional Participation
The growing acceptance of cryptocurrencies by institutional investors is expected to fuel a surge in high-frequency trading strategies. Larger capital inflows and increased market liquidity will provide more opportunities for HFT to thrive.
Technological Advancements
As technology continues to progress, traders can expect more sophisticated tools and platforms tailored for high-frequency trading in the crypto space. Machine learning and artificial intelligence are poised to play significant roles in developing better predictive models and trading strategies.
Conclusion
High-frequency trading represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving segment of the cryptocurrency market. By understanding the complexities of HFT, traders can make informed decisions and develop strategies that leverage the unique characteristics of the crypto space. Despite the risks, the potential rewards of high-frequency trading in cryptocurrencies are substantial, making it an attractive option for those willing to navigate the challenges of this fast-paced environment.